Parking is a huge factor in development. Most zoning districts have some type of parking requirement by use, which not only shapes the way our cities look, but also the way people live and interact with one another. For example, the pedestrian experience in a city can be hugely influenced by the number of lanes in a street, or whether or not there are surface parking lots everywhere. While it is very pleasant to walk by busy storefronts and restaurants, it can be daunting to walk in an area where there is little sidewalk activity. Similarly, when the ground floor of a building is mainly catering to cars, with multilane driveways or garage entrances, the pedestrian experience suffers as well. So it is very important to think of parking in relation to the urban condition.
In our software, we integrate parking calculations so you will clearly see the impact of parking requirements on the building massing, as well as in the financial projections. You can use this feature creatively, eliminating all parking if you believe you can get away with that in the zone where your project is located, or manipulating the ratios to imagine what it would be like, both in massing and financially, if you didn’t have to build for cars.
Below are some of the parameters we use, along with definitions of how we use them in our software.
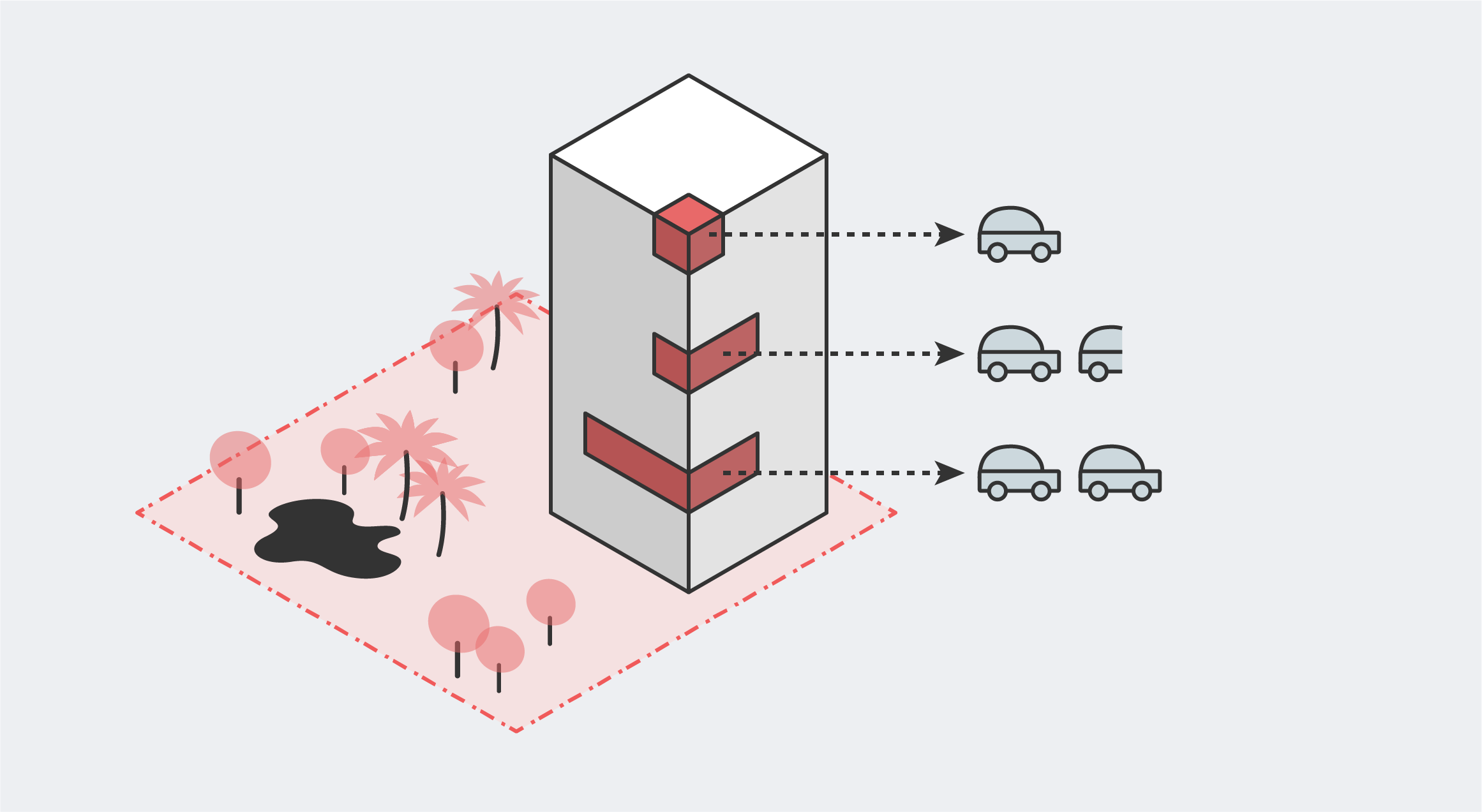
Residential Parking Requirements
In most zones, parking is required for residential uses. The number of parking spaces required is sometimes are calculated per dwelling unit, and other times per dwelling area (usually in square feet).
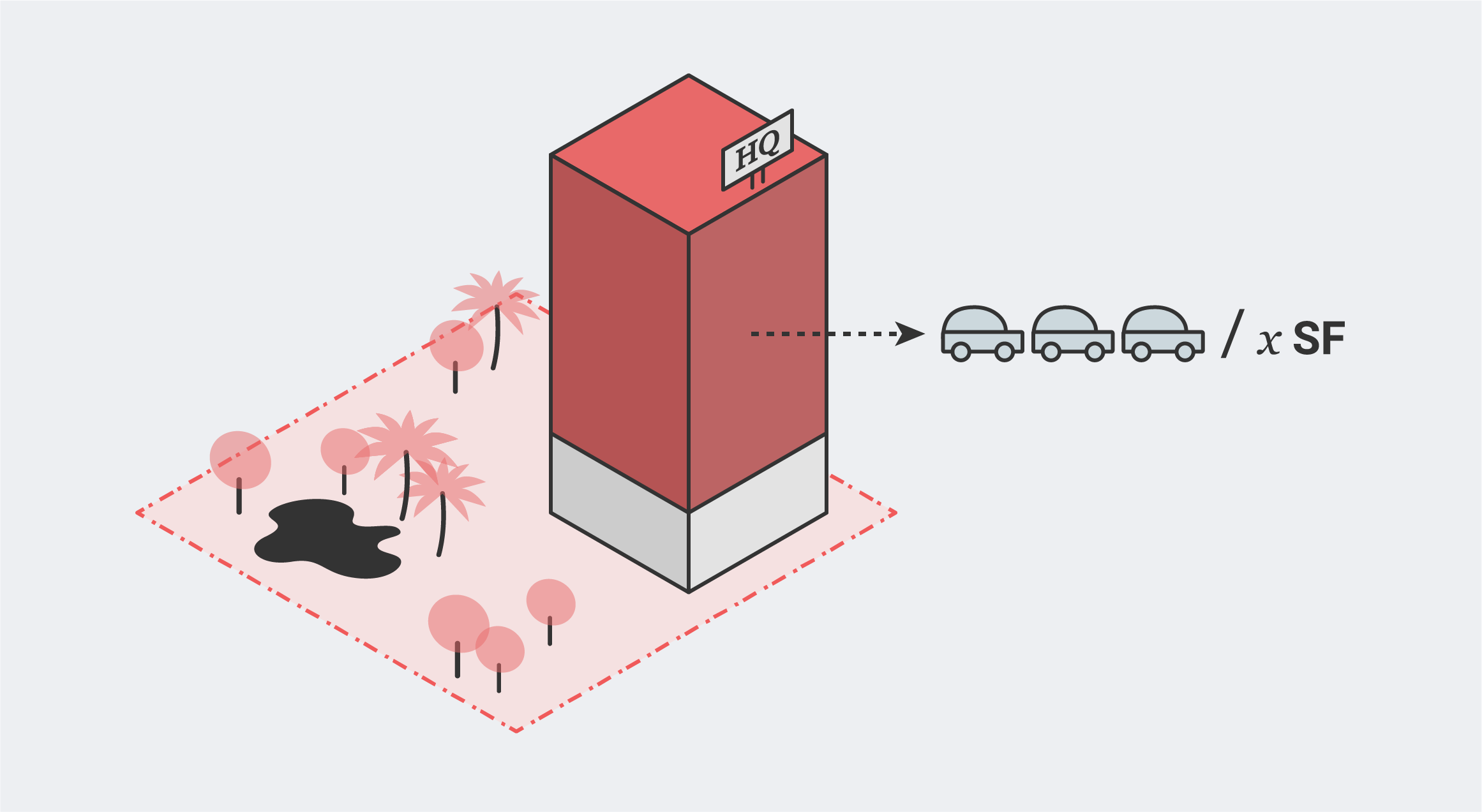

Office Parking Requirements
In most zones, parking is required for Office use. The number of parking spaces required is usually calculated by area, usually expressing the result in spaces per 1,000 square feet.
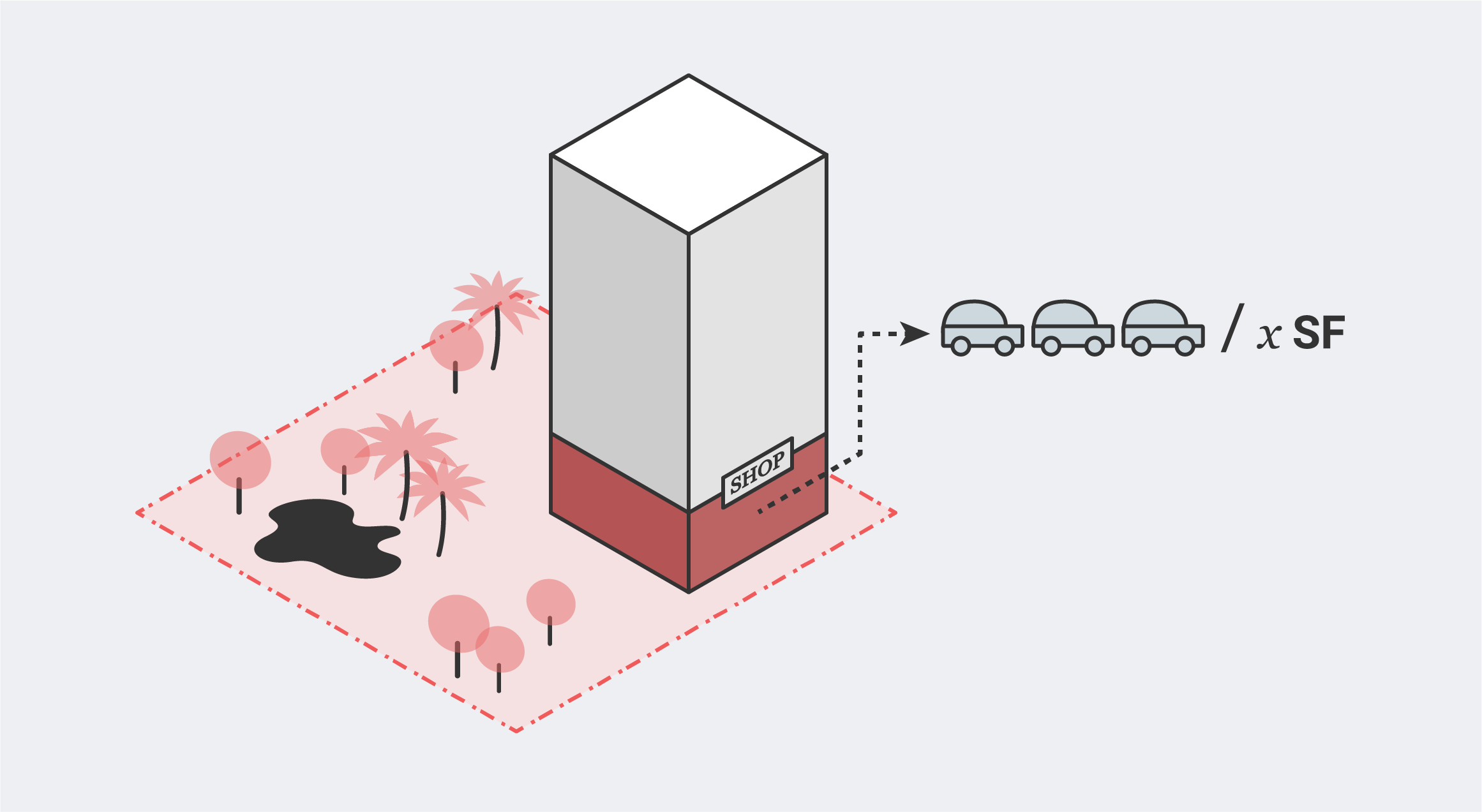

Retail Parking Requirements
In most zones, parking is required for Retail use. The number of parking spaces required is usually calculated by area, usually expressing the result in spaces per 1,000 square feet.
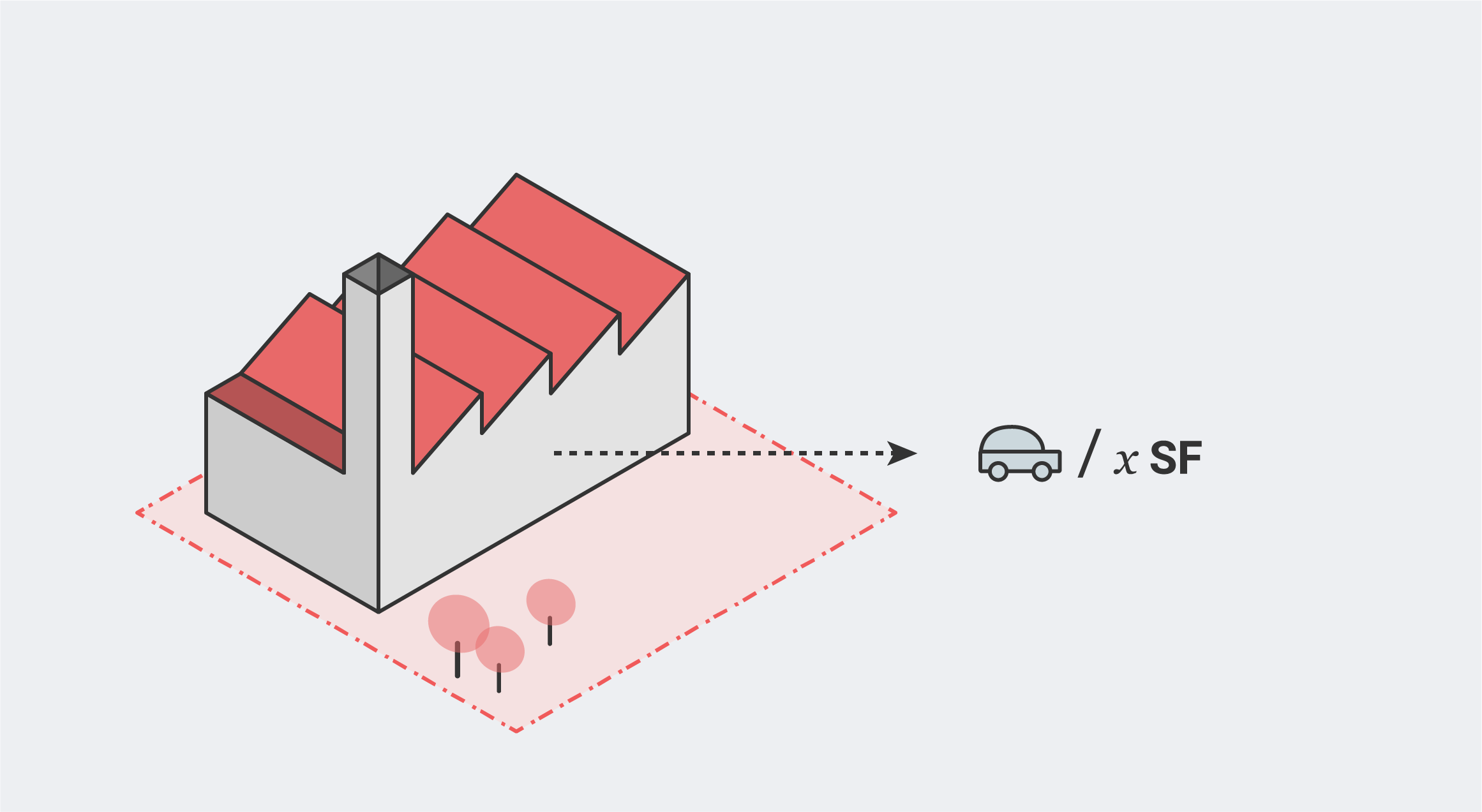

Industrial Parking Requirements
In most zones, parking is required for Industrial use. The number of parking spaces required is usually calculated by area, usually expressing the result in spaces per 1,000 square feet.






